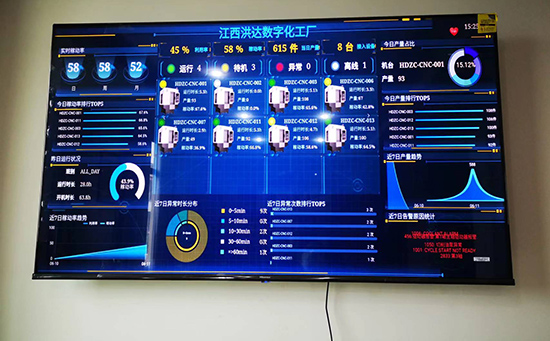
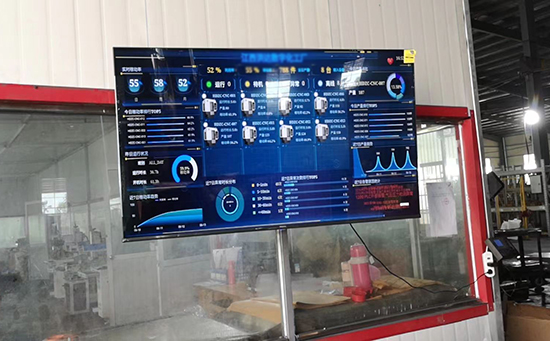
ERP系统 & MES 生产管理系统
10万用户实施案例,ERP 系统实现微信、销售、库存、生产、财务、人资、办公等一体化管理
Understanding the Basics of Excel Averages
Excel, as a powerful tool in data analysis and management, offers various functions that streamline calculations and improve efficiency. One fundamental function that users frequently utilize is the average function. This article delves into the intricacies of using averages in Excel, providing comprehensive guidance on its application and benefits.
What is the Average Function?
The average function in Excel, denoted as `AVERAGE()`, calculates the arithmetic mean of a range of numbers. This function is invaluable for analyzing data sets, as it provides a single representative value that summarizes the data’s central tendency.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Averages in Excel
To calculate an average in Excel, follow these simple steps:
1. Select the Range: Highlight the cells that contain the numbers you want to average.
2. Insert the Function: Type `=AVERAGE(` followed by selecting the range or manually entering the cell references.
3. Complete the Function: Close the parenthesis `)` and press Enter. Excel will display the calculated average.
Advanced Features and Options
Excel offers several advanced features to enhance average calculations:
– Ignoring Empty or Non-Numeric Cells: Use `AVERAGEIF()` or `AVERAGEIFS()` to calculate averages based on specific criteria.
– Weighted Averages: Utilize `SUMPRODUCT()` to calculate weighted averages by assigning different weights to each value.
– Handling Errors: Manage error values with functions like `AVERAGEIF()` combined with `ISNUMBER()` to exclude errors from calculations.
Practical Applications in Business and Finance
Averages play a crucial role in various industries:
– Financial Analysis: Calculate average monthly sales or expenses to identify trends and make informed decisions.
– Quality Control: Determine average defect rates to maintain and improve product quality.
– Educational Assessment: Analyze average test scores to evaluate student performance over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these pitfalls when working with averages in Excel:
– Including Text or Blank Cells: Ensure all included cells contain numeric data for accurate calculations.
– Misinterpreting Results: Understand the context of your data to correctly interpret average values.
– Ignoring Outliers: Consider whether outliers should be included or excluded based on your analysis goals.
Conclusion: Enhancing Data Analysis with Excel Averages
Excel’s average function simplifies complex calculations, making it an indispensable tool for professionals across various disciplines. By mastering the use of averages in Excel, users can efficiently analyze data, derive meaningful insights, and drive informed decision-making processes. Harness the power of averages in Excel to elevate your data analysis capabilities today.










 咨询顾问
咨询顾问