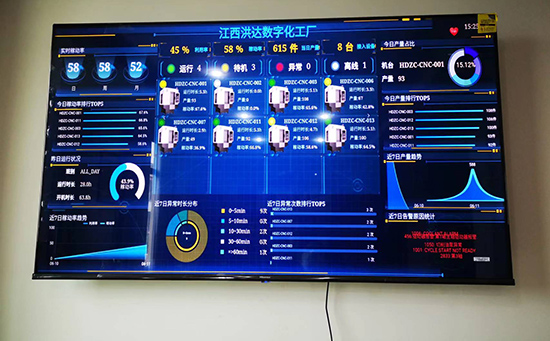
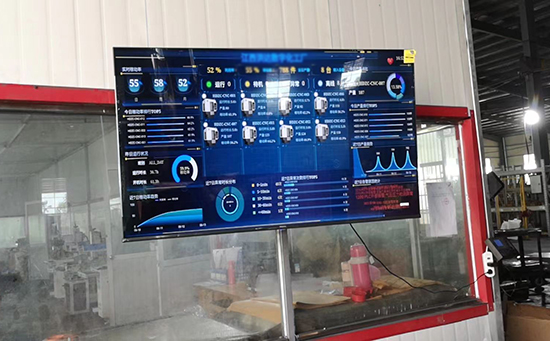
ERP系统 & MES 生产管理系统
10万用户实施案例,ERP 系统实现微信、销售、库存、生产、财务、人资、办公等一体化管理
Understanding and Calculating Averages: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of mathematics and statistics, averages play a pivotal role in summarizing data sets by providing a central value that represents the whole. Whether you’re analyzing test scores, income levels, or even temperatures, understanding how to calculate and interpret averages is essential. This guide will delve into the various types of averages, their applications, and methods of calculation to equip you with a thorough understanding.
The Basics of Averages
Averages, also known as measures of central tendency, are numerical indicators that represent a typical value within a dataset. The most commonly used types of averages include the mean, median, and mode. Each serves a distinct purpose in statistical analysis, offering insights into different aspects of the data distribution.
Mean: The Arithmetic Average
The mean is perhaps the most familiar average, calculated by summing all values in a dataset and dividing by the number of observations. It provides a balance point that considers every value equally, making it sensitive to extreme values or outliers. In practical terms, the mean is widely used in fields such as economics, science, and education to analyze trends and make predictions.
Median: The Middle Ground
Unlike the mean, which relies on numerical manipulation, the median represents the middle value when all data points are arranged in ascending or descending order. It is less influenced by outliers and extreme values, making it ideal for skewed distributions. The median is often employed in income studies, where extreme high or low incomes could distort the mean.
Mode: The Most Frequent Value
The mode identifies the most frequently occurring value in a dataset. It is particularly useful for categorical data, such as survey responses or types of products sold. Unlike the mean and median, the mode does not require numerical data and can be applied to any type of discrete distribution.
Calculating Averages: Step-by-Step
To compute these averages accurately, follow these steps:
1. Mean: Add up all values and divide by the number of values.
2. Median: Arrange values in order and identify the middle value.
3. Mode: Count occurrences of each value and identify the one with the highest frequency.
Each method has its nuances, ensuring you choose the appropriate average for your dataset based on its characteristics and objectives.
Applications Across Fields
Averages find applications across various disciplines:
– Business: Analyzing sales figures and market trends.
– Healthcare: Studying patient outcomes and treatment efficacy.
– Education: Assessing student performance and educational attainment.
Understanding how to interpret averages empowers professionals to draw meaningful conclusions from data, driving informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Averages
In conclusion, averages serve as invaluable tools in analyzing and interpreting data across diverse fields. Whether you’re a researcher, analyst, or student, mastering the nuances of mean, median, and mode equips you with the ability to derive meaningful insights from complex datasets. By employing these measures of central tendency effectively, you not only summarize data but also uncover patterns and trends that facilitate informed decision-making and problem-solving. Embrace the power of averages today to elevate your understanding and application of statistical analysis.