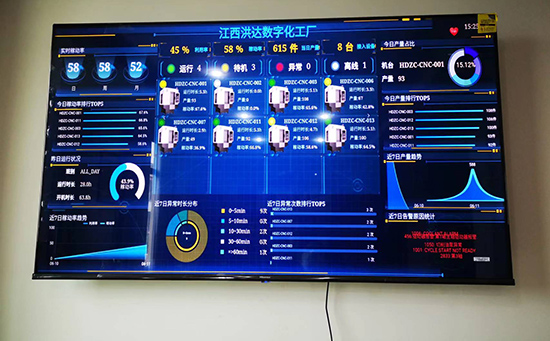
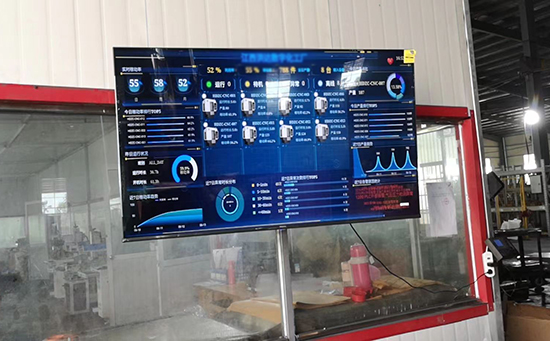
ERP系统 & MES 生产管理系统
10万用户实施案例,ERP 系统实现微信、销售、库存、生产、财务、人资、办公等一体化管理
Understanding the Average Function: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of mathematics and statistics, the average function serves as a fundamental tool for summarizing data points into a single representative value. Whether you’re analyzing test scores, market trends, or demographic data, understanding how to calculate and interpret averages is crucial. This article delves into the nuances of the average function, exploring its various types, applications, and significance in different contexts.
Types of Averages
The concept of averages encompasses several types, each with its own method of calculation and suitability for specific datasets:
Arithmetic Mean
The arithmetic mean is perhaps the most familiar type of average. It is calculated by summing all values in a dataset and dividing by the number of observations. This method is ideal for evenly distributed data sets where outliers are minimal.
Median
The median represents the middle value when all values are arranged in ascending or descending order. This average is less influenced by extreme values, making it suitable for skewed distributions.
Mode
The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a dataset. It is particularly useful for categorical data where identifying the most common category is important.
Applications in Data Analysis
Economic Analysis
In economics, averages help economists understand trends in GDP growth, inflation rates, and consumer spending. By calculating averages over time, economists can make informed predictions about future economic conditions.
Educational Assessment
Educators use averages to evaluate student performance across subjects or within specific classes. Averages provide a snapshot of overall academic achievement and help identify areas where additional support may be needed.
Healthcare Metrics
In healthcare, averages are crucial for assessing patient outcomes, such as average recovery times or average treatment effectiveness. These metrics aid healthcare providers in improving patient care and allocating resources effectively.
Challenges and Considerations
While averages offer valuable insights, they also come with limitations that must be considered:
Skewed Data
Data sets with outliers or highly skewed distributions may distort average values, leading to misleading conclusions if not properly analyzed.
Contextual Interpretation
Averages should always be interpreted within the context of the data and the specific question being addressed. Failing to do so can result in misinterpretations and erroneous decisions.
Sample Size
The size of the sample used to calculate averages can significantly impact their reliability. Larger samples generally provide more accurate average values than smaller ones.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the average function is essential for anyone involved in data analysis across various fields. By grasping the nuances of arithmetic mean, median, and mode, one can derive meaningful insights from datasets ranging from economic indicators to healthcare outcomes. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, mastering the use of averages enhances your ability to make informed decisions based on data-driven evidence. Explore further applications of averages in your specific domain to harness their full potential.
This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge to effectively utilize averages in your analytical endeavors. Embrace the power of averages to unlock deeper insights and drive informed decision-making in your respective field.