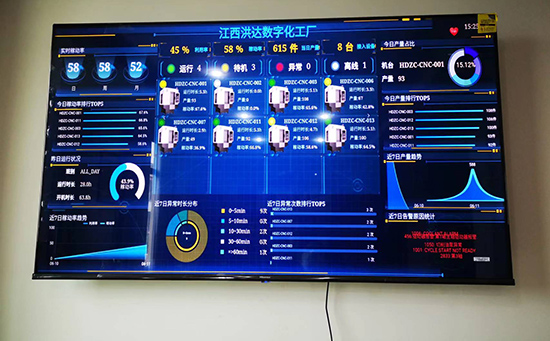
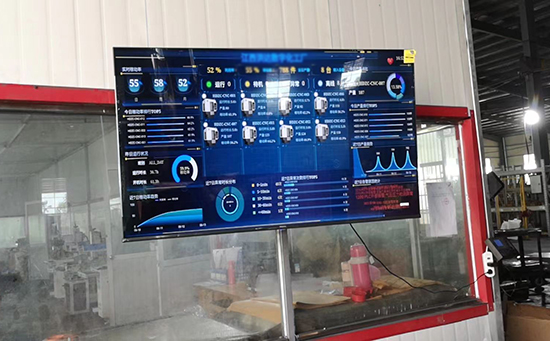
ERP系统 & MES 生产管理系统
10万用户实施案例,ERP 系统实现微信、销售、库存、生产、财务、人资、办公等一体化管理
Understanding the Maintenance Costs of an ERP Management System
In today’s dynamic business landscape, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and facilitating data-driven decision-making. However, beyond the initial implementation, businesses must be prepared to allocate resources for the ongoing maintenance of their ERP systems. This article delves into the various factors influencing ERP maintenance costs and provides insights into estimating these expenses effectively.
Factors Influencing ERP Maintenance Costs
1. Software Updates and Upgrades
ERP systems undergo periodic updates and upgrades to incorporate new features, enhancements, and security patches. These updates ensure that the system remains compatible with evolving technologies and business requirements. The costs associated with software updates and upgrades typically include licensing fees, implementation expenses, and testing efforts to validate compatibility and functionality.
2. Technical Support and Training
Effective technical support is essential for addressing issues promptly and maintaining system uptime. Many ERP vendors offer support packages ranging from basic to premium tiers, with corresponding costs. Additionally, ongoing training programs are necessary to empower users with the skills required to leverage the full potential of the ERP system. Training expenses may vary based on the complexity of the system and the number of users requiring instruction.
3. Customization and Integration
Businesses often customize their ERP systems to align with unique workflows and business processes. However, customization introduces complexities that may necessitate ongoing maintenance and support. Moreover, as businesses expand or adopt new technologies, integrating the ERP system with other software applications becomes crucial. Integration efforts incur additional costs related to development, testing, and ongoing maintenance to ensure seamless data flow between systems.
Methods of Estimating Maintenance Costs
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
TCO analysis involves evaluating all direct and indirect costs associated with owning and operating an ERP system over its lifecycle. This comprehensive approach considers not only initial implementation costs but also ongoing expenses such as maintenance, support, training, and upgrades. By calculating TCO, businesses can make informed decisions about budget allocation and resource planning for ERP maintenance.
5. Vendor Contracts and Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Negotiating favorable vendor contracts with clear SLAs is crucial for managing ERP maintenance costs effectively. SLAs define the scope of support services, response times for issue resolution, and escalation procedures. By establishing transparent agreements with ERP vendors, businesses can mitigate the risk of unexpected expenses and ensure predictable maintenance costs over time.
6. Continuous Improvement Initiatives
Embracing a culture of continuous improvement can help optimize ERP maintenance processes and minimize costs. By regularly assessing system performance, identifying areas for enhancement, and implementing efficiency measures, businesses can streamline maintenance activities and maximize the return on investment in their ERP systems. Additionally, leveraging emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and automation can drive further efficiencies and reduce manual intervention in maintenance tasks.
In Conclusion
As businesses increasingly rely on ERP systems to drive operational excellence, understanding and budgeting for maintenance costs are paramount. By accounting for factors such as software updates, technical support, customization, and integration, businesses can develop accurate estimates of ERP maintenance expenses. Employing methodologies like TCO analysis, negotiating vendor contracts with clear SLAs, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement can further optimize maintenance processes and ensure the long-term success of ERP investments. Remember, proactive maintenance is key to maximizing the value derived from ERP systems and staying ahead in today’s competitive market landscape.










 咨询顾问
咨询顾问